محصولات
آند های فداشونده
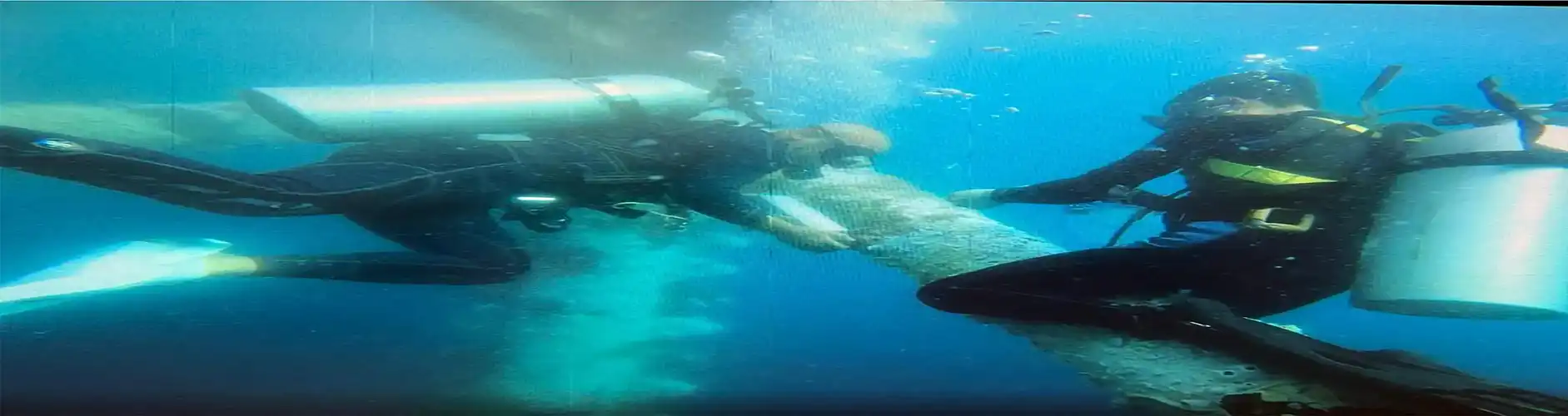
محصولات صنایع دریایی
آند DSA
آند های تزریق جریان
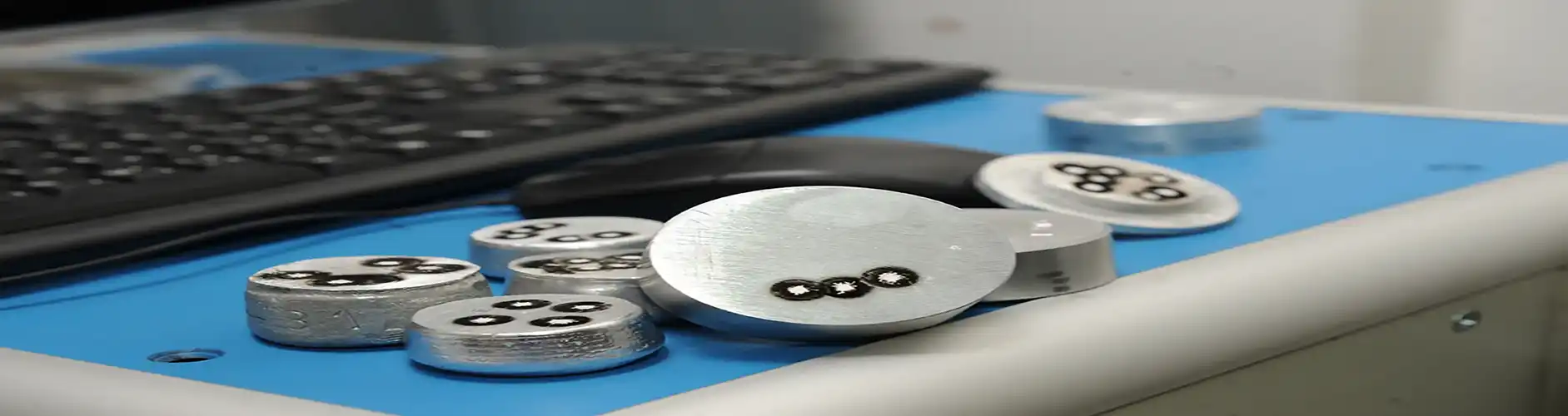
الکترود های مرجع و تجهیزات جانبی
معرفی شرکت برناگداز
شرکت برناگداز در سال 1383 به منظور گسترش فعالیتهای شرکت برناالکترونیک در بخش تولید انواع آندهای حفاظت کاتدی به عنوان یک شرکت مستقل تأسیس گردید.
محصولات شرکت برناگداز
شرکت برناگداز با تولید محصولات مرتبط با حفاظت کاتدی برطبق استانداردهای ملی و بینالمللی، در رقابت با انواع محصولات ایرانی و خارجی جایگاهی ممتاز را به خود اختصاص داده است که تأییدیهها و گواهینامه های دریافت شده از مؤسسات مختلف مؤید این مطلب است.